Understanding Latency in HLS and Why RTMP Still Matters
When it comes to live streaming, latency—the delay between a live event and its playback—is a critical factor. While HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) has become the default for delivering video to audiences on mobile devices and computers, it comes with a notable drawback: latency. Meanwhile, Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) continues to play a vital role in live streaming workflows, particularly for ingesting live feeds. This article unpacks the latency issue in HLS, why RTMP remains relevant, and how the two technologies complement each other.
The Latency Trade-Off in HLS
HLS is popular because of its adaptability and compatibility. It breaks video streams into small chunks, typically between 6 and 10 seconds long, which are then delivered via HTTP. This segmented approach ensures smooth playback across various devices and network conditions. However, the segmentation and buffering introduce a delay ranging from 6 to 30 seconds, depending on the configuration.
For most scenarios, such as live TV broadcasts or virtual events, this latency is manageable. One broadcaster shared an anecdote about live-streaming a cultural festival in Nairobi using HLS. Despite the 10-second delay, the audience praised the stream’s quality and accessibility. However, for applications like live sports betting or real-time auctions, even a few seconds of delay can make HLS impractical.
RTMP: The Low-Latency Workhorse
RTMP was designed for low-latency streaming, making it ideal for real-time interactions. Although its direct use has diminished due to the decline of Flash Player, RTMP remains integral as an input protocol for streaming servers. RTMP allows for near-instant ingestion of live feeds, which can then be converted into HLS for playback.
Consider the case of a sports broadcaster who needed a solution for streaming live games to a global audience. By using RTMP for ingestion and HLS for delivery, they achieved a balance between low latency during the encoding process and wide compatibility for viewers. The initial latency of HLS didn’t hinder the broadcast, as it wasn’t a betting event.
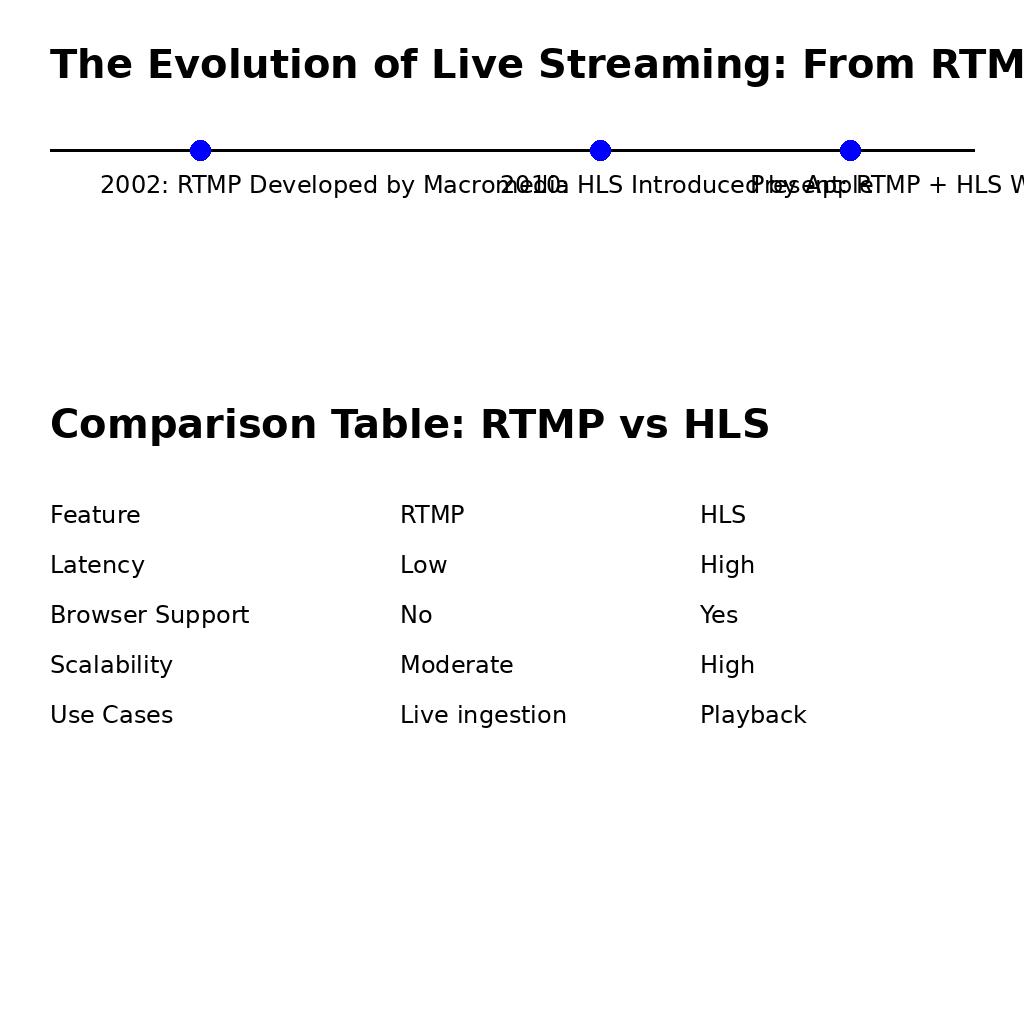
Comparing RTMP and HLS
Here’s a quick comparison of RTMP and HLS based on key metrics:
Metric
RTMP
HLS
Latency
Low
High
Browser Support
No
Yes
Use Cases
Ingest, low-latency workflows
Playback, high compatibility
Scalability
Moderate
High
Why RTMP Still Matters
RTMP’s ability to ingest live streams with minimal delay ensures it remains a cornerstone of live streaming workflows. Its role has shifted from end-to-end protocol to a backend solution feeding HLS or DASH outputs. This combination is ideal for:
Live Events: RTMP handles ingestion, and HLS ensures broad device support.
TV Broadcasts: RTMP minimizes delays during production, while HLS delivers high-quality streams to viewers.
Educational Content: Live lectures benefit from RTMP’s low-latency input, with HLS providing seamless playback.
Solving HLS Latency Issues
Although HLS latency can’t be eliminated entirely, there are ways to minimize it:
Reduce Segment Duration: By lowering the chunk size to 2-4 seconds, latency can be significantly reduced.
Use Low-Latency HLS (LL-HLS): This version of HLS decreases delay by allowing clients to fetch data while segments are still being generated.
Optimize Encoding Settings: Faster encoding reduces the time required to process live streams.
A broadcaster once shared how adopting LL-HLS cut their stream’s delay from 15 seconds to just under 4 seconds, making it more suitable for interactive events.
The RTMP-HLS Synergy
RTMP and HLS are not competitors but collaborators. RTMP’s real-time performance and HLS’s playback compatibility make them complementary. In a typical workflow, RTMP is used for ingestion by a server like NGINX or Wowza, which then converts the stream to HLS for distribution.
Final Thoughts
Latency is an inevitable part of live streaming, but understanding and optimizing your workflow can make it manageable. RTMP’s role in reducing latency during ingestion and HLS’s adaptability for playback make them a powerful duo. Whether you’re streaming a live concert, a corporate event, or a sports match, leveraging these technologies effectively ensures a seamless experience for your audience.
Hashtags:
#LowLatency #Streaming #RTMPHLSWorkflow #Broadcasting #NGINX #WowzaStreaming